Overview
Why build the Proof of Neutrality Relay?
Ethereum’s credible neutrality and decentralization of consensus is under threat from centralized relays and censorship caused by MEV’s infrastructure and its impact on consensus. The PoN Relay’s decentralized infrastructure is necessary to create a world of permissionless communication between block-builders and block proposers.
What is the Proof of Neutrality Relay?
The Proof of Neutrality (PoN) Relay is a decentralized, permissionless, and neutral middleware run by validators to participate in the market for block-building and exchange. The PoN Relay to issues surrounding centralized relays and implements Proposer-Builder Separation theory (PBS) put forward by Vitalik Buterin in its design.
In a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) environment, validators and MEV will become more closely linked due to the appeal of increasing their staking rewards though MEV. MEV rewards will have growing importance as more validators join and staking participation increases, causing staking rewards to inevitably decrease. The PoN Relay maximizes validator rewards through the selling of blockspace to an open market, allowing for consistent MEV payouts from the Adaptive PBS Smoothing Pool.
What is Proposer-Builder Separation (PBS)?
PBS focuses on the relationship between the protocol and non-protocol actors involved in the maintenance and operation of a blockchain, and the necessary separation to maintain a decentralized consensus. Block builders become responsible for creating blocks and offering them to the block proposer in each slot. The block proposer cannot see the contents of the block, they simply choose the most profitable one, paying a fee to the block builder before sending the block to its peers. This is an important upgrade in decentralized infrastructure as it keeps actors blindly working together.
The PoN Relay offers a PBS-centric middleware solution that establishes a decentralized exchange for blockspace. Proposers in the PoN Relay are able to accept the transaction bundle with the highest fee, while outside actors called block-builders construct bundles of complete block contents that include a fee for the proposer but keep the contents of the block confidential.
How does the Proof of Neutrality Relay Work?
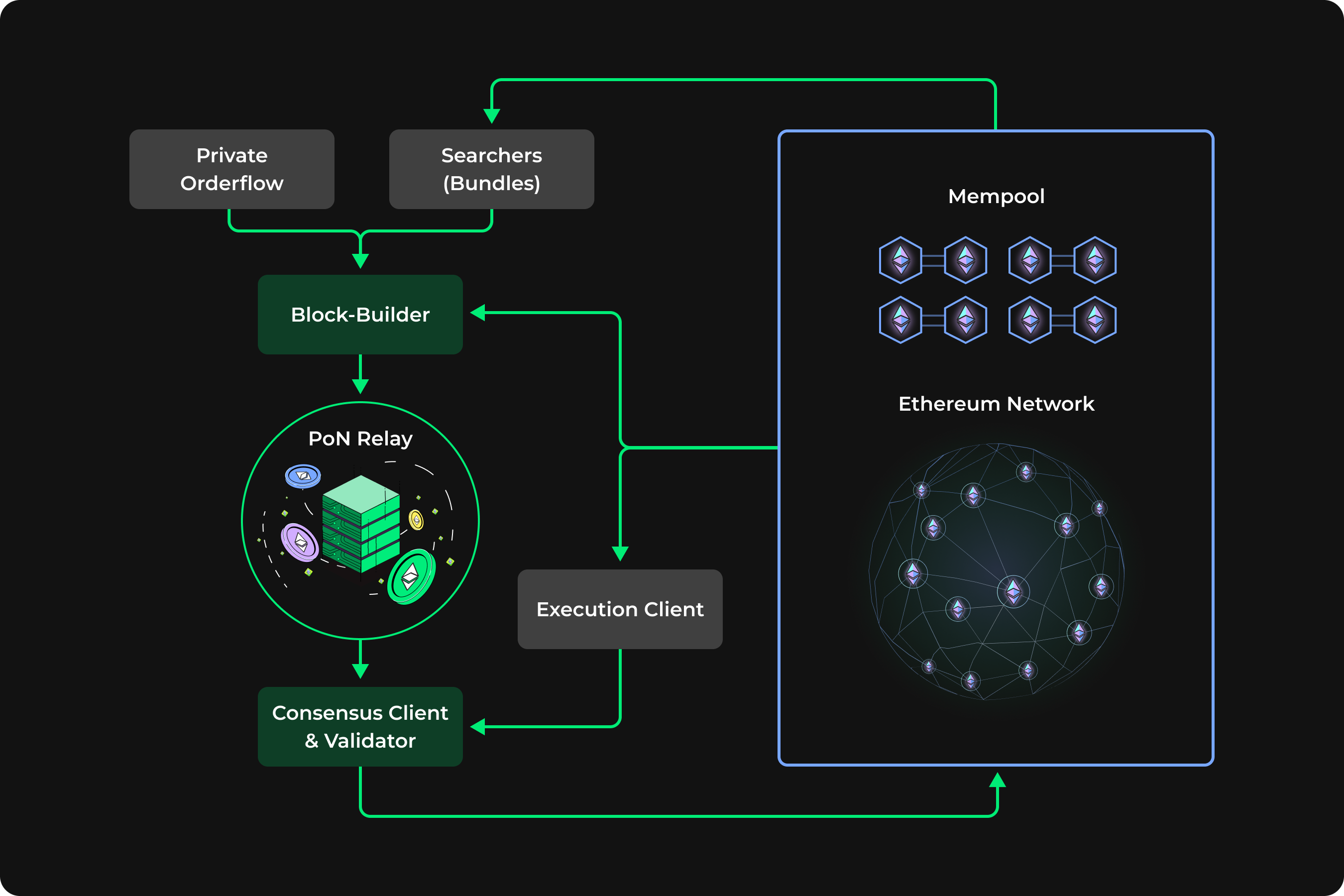
In the Ethereum Proof-of-Stake (PoS) system, node operators use three essential pieces of software components: the validator client, the execution client, and the consensus client. The PoN Relay is an additional open-source software that seamlessly integrates with the consensus client, allowing for connection to a network of block-builders and the outsourcing of block-building. Additionally, it uses zero knowledge proofs and encrypted communication to facilitate the builder’s request for a validator. This ensures guaranteed validator payment inclusion in a block while also keeping block content unrevealed.
Block-builders create full blocks aiming for the optimal MEV extraction and equitable distribution of rewards. Once they are done, the blocks are sent to relays. The PoN Relay selects the highest tipping block received from various builders, submits it to the block proposer, and the consensus client then sends it to the Ethereum network for verification and block inclusion.
Reporters are a novel addition and essential for a decentralized infrastructure to run smoothly. In the PoN Relay, reporters monitor the actions of builders and proposers to ensure that there is no malicious behavior or wrongdoing. If a violation occurs, the reporter can submit a report and earn ETH for securing the protocol.